 |
| January 09, 2024 | Volume 20 Issue 01 |
Motion Control News & Products
Designfax weekly eMagazine
Archives
Partners
Manufacturing Center
Product Spotlight
Modern Applications News
Metalworking Ideas For
Today's Job Shops
Tooling and Production
Strategies for large
metalworking plants
Linear guide system corrects misalignments
 Bishop-Wisecarver's UtiliTrak® linear guide system includes vee rails for precision and open rails for misalignment float to provide smooth and accurate motion on inaccurate structures. Because precise parallelism is difficult to achieve, it is not uncommon for mounting surfaces to be slightly out of parallel. UtiliTrak's design compensates for mounting errors and does not require absolute parallelism for accurate operation. Genius.
Bishop-Wisecarver's UtiliTrak® linear guide system includes vee rails for precision and open rails for misalignment float to provide smooth and accurate motion on inaccurate structures. Because precise parallelism is difficult to achieve, it is not uncommon for mounting surfaces to be slightly out of parallel. UtiliTrak's design compensates for mounting errors and does not require absolute parallelism for accurate operation. Genius.
Learn more.
Universal Robots emerges as preferred robotics platform for AI solutions at Automate 2024
 At North America's largest automation show (Chicago, May 6-9), cobot pioneer Universal Robots will redefine the frontiers of physical AI, showcasing how the "ChatGPT moment for robots" has arrived in a wide range of applications. Automate attendees will also experience how Universal Robots' newest cobot models, the UR20 and UR30, automate tasks with increased payload, reach, and torque.
At North America's largest automation show (Chicago, May 6-9), cobot pioneer Universal Robots will redefine the frontiers of physical AI, showcasing how the "ChatGPT moment for robots" has arrived in a wide range of applications. Automate attendees will also experience how Universal Robots' newest cobot models, the UR20 and UR30, automate tasks with increased payload, reach, and torque.
Learn more.
Multi-stage mini vacuum pumps: Max performance
 Designed to meet the demanding needs of industrial users, the CMS M series mini vacuum pump from COVAL combines robustness, performance, and modularity, offering an optimum solution for applications requiring high suction flow rates, such as gripping porous parts, emptying tanks, or material handling when integrated into vacuum grippers. Thanks to their ultra-compact design and optimized multi-stage Venturi system, these pumps guarantee powerful suction flows up to 19.42 SCFM, while reducing compressed air consumption in a compact footprint.
Designed to meet the demanding needs of industrial users, the CMS M series mini vacuum pump from COVAL combines robustness, performance, and modularity, offering an optimum solution for applications requiring high suction flow rates, such as gripping porous parts, emptying tanks, or material handling when integrated into vacuum grippers. Thanks to their ultra-compact design and optimized multi-stage Venturi system, these pumps guarantee powerful suction flows up to 19.42 SCFM, while reducing compressed air consumption in a compact footprint.
Learn more.
Choosing a stepper motor: PM or hybrid?
 Lin Engineering stepper motors are widely used in various applications that require precise control of motion, such as in robotics, 3D printing, CNC machines, and medical equipment. There are two main types of stepper motors: permanent magnet (PM) and hybrid. Learn the differences, advantages, and when to use one type or the other.
Lin Engineering stepper motors are widely used in various applications that require precise control of motion, such as in robotics, 3D printing, CNC machines, and medical equipment. There are two main types of stepper motors: permanent magnet (PM) and hybrid. Learn the differences, advantages, and when to use one type or the other.
Read this informative Lin Engineering article.
Top Product: Integrated servo system is 20% smaller than standalone unit
 Applied Motion Products has introduced the MDX+ series, a family of low-voltage servo systems that integrate a servo drive, motor, and encoder into one package. This all-in-one drive unit is an ideal solution for manufacturers in logistics, AGV, medical, semiconductor, the solar industries, and many others.
Applied Motion Products has introduced the MDX+ series, a family of low-voltage servo systems that integrate a servo drive, motor, and encoder into one package. This all-in-one drive unit is an ideal solution for manufacturers in logistics, AGV, medical, semiconductor, the solar industries, and many others.
Read the full article.
Overhung load adaptors provide load support and contamination protection
 Overhung load adaptors (OHLA) provide both overhung radial and axial load support to protect electrified mobile equipment motors from heavy application loads, extending the lifetime of the motor and alleviating the cost of downtime both from maintenance costs and loss of production. They seal out dirt, grime, and other contaminants too. Zero-Max OHLAs are available in an extensive offering of standard models (including Extra-Duty options) for typical applications or customized designs.
Overhung load adaptors (OHLA) provide both overhung radial and axial load support to protect electrified mobile equipment motors from heavy application loads, extending the lifetime of the motor and alleviating the cost of downtime both from maintenance costs and loss of production. They seal out dirt, grime, and other contaminants too. Zero-Max OHLAs are available in an extensive offering of standard models (including Extra-Duty options) for typical applications or customized designs.
Learn more.
Why choose electric for linear actuators?
 Tolomatic has been delivering a new type of linear motion technology that is giving hydraulics a run for its money. Learn the benefits of electric linear motion systems, the iceberg principle showing total cost of ownership, critical parameters of sizing, and conversion tips.
Tolomatic has been delivering a new type of linear motion technology that is giving hydraulics a run for its money. Learn the benefits of electric linear motion systems, the iceberg principle showing total cost of ownership, critical parameters of sizing, and conversion tips.
Get this informative e-book. (No registration required)
New AC hypoid inverter-duty gearmotors
 Bodine Electric Company introduces 12 new AC inverter-duty hypoid hollow shaft gearmotors. These type 42R-25H2 and 42R-30H3 drives combine an all-new AC inverter-duty, 230/460-VAC motor with two hypoid gearheads. When used with an AC inverter (VFD) control, these units deliver maintenance-free and reliable high-torque output. They are ideal for conveyors, gates, packaging, and other industrial automation equipment that demands both high torque and low power consumption from the driving gearmotor.
Bodine Electric Company introduces 12 new AC inverter-duty hypoid hollow shaft gearmotors. These type 42R-25H2 and 42R-30H3 drives combine an all-new AC inverter-duty, 230/460-VAC motor with two hypoid gearheads. When used with an AC inverter (VFD) control, these units deliver maintenance-free and reliable high-torque output. They are ideal for conveyors, gates, packaging, and other industrial automation equipment that demands both high torque and low power consumption from the driving gearmotor.
Learn more.
Next-gen warehouse automation: Siemens, Universal Robots, and Zivid partner up
 Universal Robots, Siemens, and Zivid have created a new solution combining UR's cobot arms with Siemens' SIMATIC Robot Pick AI software and Zivid's 3D sensors to create a deep-learning picking solution for warehouse automation and intra-logistics fulfillment. It works regardless of object shape, size, opacity, or transparency and is a significant leap in solving the complex challenges faced by the logistics and e-commerce sectors.
Universal Robots, Siemens, and Zivid have created a new solution combining UR's cobot arms with Siemens' SIMATIC Robot Pick AI software and Zivid's 3D sensors to create a deep-learning picking solution for warehouse automation and intra-logistics fulfillment. It works regardless of object shape, size, opacity, or transparency and is a significant leap in solving the complex challenges faced by the logistics and e-commerce sectors.
Read the full article.
Innovative DuoDrive gear and motor unit is UL/CSA certified
 The DuoDrive integrated gear unit and motor from NORD DRIVE-SYSTEMS is a compact, high-efficiency
solution engineered for users in the fields of intralogistics, pharmaceutical, and the food and beverage industries. This drive combines a IE5+ synchronous motor and single-stage helical gear unit into one compact housing with a smooth, easy-to-clean surface. It has a system efficiency up to 92% and is available in two case sizes with a power range of 0.5 to 4.0 hp.
The DuoDrive integrated gear unit and motor from NORD DRIVE-SYSTEMS is a compact, high-efficiency
solution engineered for users in the fields of intralogistics, pharmaceutical, and the food and beverage industries. This drive combines a IE5+ synchronous motor and single-stage helical gear unit into one compact housing with a smooth, easy-to-clean surface. It has a system efficiency up to 92% and is available in two case sizes with a power range of 0.5 to 4.0 hp.
Learn more.
BLDC flat motor with high output torque and speed reduction
 Portescap's 60ECF brushless DC slotted flat motor is the newest frame size to join its flat motor portfolio. This 60-mm BLDC motor features a 38.2-mm body length and an outer-rotor slotted configuration with an open-body design, allowing it to deliver improved heat management in a compact package. Combined with Portescap gearheads, it delivers extremely high output torque and speed reduction. Available in both sensored and sensorless options. A great choice for applications such as electric grippers and exoskeletons, eVTOLs, and surgical robots.
Portescap's 60ECF brushless DC slotted flat motor is the newest frame size to join its flat motor portfolio. This 60-mm BLDC motor features a 38.2-mm body length and an outer-rotor slotted configuration with an open-body design, allowing it to deliver improved heat management in a compact package. Combined with Portescap gearheads, it delivers extremely high output torque and speed reduction. Available in both sensored and sensorless options. A great choice for applications such as electric grippers and exoskeletons, eVTOLs, and surgical robots.
Learn more and view all the specs.
Application story: Complete gearbox and coupling assembly for actuator system
 Learn how GAM engineers not only sized and selected the appropriate gear reducers and couplings required to drive two ball screws in unison using a single motor, but how they also designed the mounting adapters necessary to complete the system. One-stop shopping eliminated unnecessary components and resulted in a 15% reduction in system cost.
Learn how GAM engineers not only sized and selected the appropriate gear reducers and couplings required to drive two ball screws in unison using a single motor, but how they also designed the mounting adapters necessary to complete the system. One-stop shopping eliminated unnecessary components and resulted in a 15% reduction in system cost.
Read this informative GAM blog.
Next-gen motor for pump and fan applications
 The next evolution of the award-winning Aircore EC motor from Infinitum is a high-efficiency system designed to power commercial and industrial applications such as HVAC fans, pumps, and data centers with less energy consumption, reduced emissions, and reduced waste. It features an integrated variable frequency drive and delivers upward of 93% system efficiency, as well as class-leading power and torque density in a low-footprint package that is 20% lighter than the previous version. Four sizes available.
The next evolution of the award-winning Aircore EC motor from Infinitum is a high-efficiency system designed to power commercial and industrial applications such as HVAC fans, pumps, and data centers with less energy consumption, reduced emissions, and reduced waste. It features an integrated variable frequency drive and delivers upward of 93% system efficiency, as well as class-leading power and torque density in a low-footprint package that is 20% lighter than the previous version. Four sizes available.
Learn more.
Telescoping linear actuators for space-constrained applications
 Rollon's new TLS telescoping linear actuators enable long stroke lengths with minimal closed lengths, which is especially good for applications with minimal vertical clearance. These actuators integrate seamlessly into multi-axis systems and are available in two- or three-stage versions. Equipped with a built-in automated lubrication system, the TLS Series features a synchronized drive system, requiring only a single motor to achieve motion. Four sizes (100, 230, 280, and 360) with up to 3,000-mm stroke length.
Rollon's new TLS telescoping linear actuators enable long stroke lengths with minimal closed lengths, which is especially good for applications with minimal vertical clearance. These actuators integrate seamlessly into multi-axis systems and are available in two- or three-stage versions. Equipped with a built-in automated lubrication system, the TLS Series features a synchronized drive system, requiring only a single motor to achieve motion. Four sizes (100, 230, 280, and 360) with up to 3,000-mm stroke length.
Learn more.
Competitively priced long-stroke parallel gripper
 The DHPL from Festo is a new generation of pneumatic long-stroke grippers that offers a host of advantages for high-load and high-torque applications. It is interchangeable with competitive long-stroke grippers and provides the added benefits of lighter weight, higher precision, and no maintenance. It is ideal for gripping larger items, including stacking boxes, gripping shaped parts, and keeping bags open. It has high repetition accuracy due to three rugged guide rods and a rack-and-pinion design.
The DHPL from Festo is a new generation of pneumatic long-stroke grippers that offers a host of advantages for high-load and high-torque applications. It is interchangeable with competitive long-stroke grippers and provides the added benefits of lighter weight, higher precision, and no maintenance. It is ideal for gripping larger items, including stacking boxes, gripping shaped parts, and keeping bags open. It has high repetition accuracy due to three rugged guide rods and a rack-and-pinion design.
Learn more.
NASA and DARPA developing nuclear rocket engine for future Mars missions
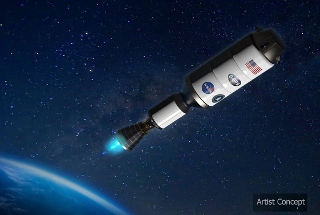
Artist concept of Demonstration for Rocket to Agile Cislunar Operations (DRACO) spacecraft, which will demonstrate a nuclear thermal rocket engine. Nuclear thermal propulsion technology could be used for future NASA crewed missions to Mars. [Credit: DARPA]
NASA and the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) announced Jan. 24, 2023, a collaboration to demonstrate a nuclear thermal rocket engine in space, an enabling capability for NASA crewed missions to Mars.
NASA and DARPA will partner on the Demonstration Rocket for Agile Cislunar Operations, or DRACO, program. The non-reimbursable agreement, designed to benefit both agencies, outlines roles, responsibilities, and processes aimed at speeding up development efforts.
"NASA will work with our long-term partner, DARPA, to develop and demonstrate advanced nuclear thermal propulsion technology as soon as 2027. With the help of this new technology, astronauts could journey to and from deep space faster than ever -- a major capability to prepare for crewed missions to Mars," said NASA Administrator Bill Nelson.
Using a nuclear thermal rocket allows for faster transit time, reducing risk for astronauts. Reducing transit time is a key component for human missions to Mars, as longer trips require more supplies and more robust systems. Maturing faster, more efficient transportation technology will help NASA meet its Moon to Mars Objectives.
To date, only robotic explorers have traveled to Mars, without the need for returning to Earth. Waiting for optimal planetary alignment for the return trip would require astronauts to loiter at Mars for more than a year, stretching the round-trip mission to more than three years.
NASA's goal is to minimize the time the crew travels between Earth and Mars to as close to two years as is practical. Space nuclear propulsion systems could enable shorter total mission times and provide enhanced flexibility and efficiency for mission designers.

Illustration of a Mars transit habitat and nuclear propulsion system that could one day take astronauts to Mars. [Credit: NASA]
Other benefits to space travel include increased science payload capacity and higher power for instrumentation and communication. In a nuclear thermal rocket engine, a fission reactor is used to generate extremely high temperatures. The engine transfers the heat produced by the reactor to a liquid propellant, which is expanded and exhausted through a nozzle to propel the spacecraft. Nuclear thermal rockets can be three or more times more efficient than conventional chemical propulsion.
Under the agreement, NASA's Space Technology Mission Directorate (STMD) will lead technical development of the nuclear thermal engine to be integrated with DARPA's experimental spacecraft. DARPA is acting as the contracting authority for the development of the entire stage and the engine, which includes the reactor. DARPA will lead the overall program including rocket systems integration and procurement, approvals, scheduling, and security; cover safety and liability; and ensure overall assembly and integration of the engine with the spacecraft. Over the course of the development, NASA and DARPA will collaborate on assembly of the engine before the in-space demonstration as early as 2027.
"DARPA and NASA have a long history of fruitful collaboration in advancing technologies for our respective goals, from the Saturn V rocket that took humans to the Moon for the first time to robotic servicing and refueling of satellites," said Dr. Stefanie Tompkins, director, DARPA. "The space domain is critical to modern commerce, scientific discovery, and national security. The ability to accomplish leap-ahead advances in space technology through the DRACO nuclear thermal rocket program will be essential for more efficiently and quickly transporting material to the Moon and, eventually, people to Mars."
The last nuclear thermal rocket engine tests conducted by the United States occurred more than 50 years ago under NASA's Nuclear Engine for Rocket Vehicle Application and Rover projects.
"With this collaboration, we will leverage our expertise gained from many previous space nuclear power and propulsion projects," said Jim Reuter, associate administrator for STMD. "Recent aerospace materials and engineering advancements are enabling a new era for space nuclear technology, and this flight demonstration will be a major achievement toward establishing a space transportation capability for an Earth-Moon economy."
NASA, the Department of Energy (DOE), and industry are also developing advanced space nuclear technologies for multiple initiatives to harness power for space exploration. Through NASA's Fission Surface Power project, DOE awarded three commercial design efforts to develop nuclear power plant concepts that could be used on the surface of the Moon and, later, Mars.
NASA and DOE are working another commercial design effort to advance higher temperature fission fuels and reactor designs as part of a nuclear thermal propulsion engine. These design efforts are still under development to support a longer-range goal for increased engine performance and will not be used for the DRACO engine.
NASA and DOE efforts
NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, AL, leads the agency's space nuclear propulsion project in partnership with a DOE team that includes scientists and engineers from Idaho National Laboratory, Los Alamos National Laboratory, and Oak Ridge National Laboratory. STMD's Technology Demonstration Missions program funds the technology development.
Nuclear electric propulsion builds on NASA's work maturing solar electric propulsion thrusters and systems for Artemis, as well as the development of fission power for the lunar surface. Significant investment has also been made in relevant fuel and reactor technologies for small, terrestrial reactors that could be adapted to space reactors to power electric propulsion. The U.S. government's aim to establish a fuel fabrication capability has a range of applications, including nuclear propulsion and fission surface power.
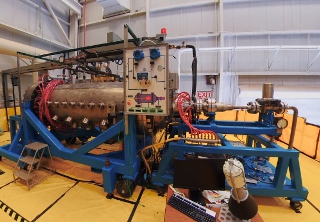
The Nuclear Thermal Rocket Element Environmental Simulator at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, AL, tests nuclear rocket fuel prototypes using non-nuclear heating instead of fission. [Credit: NASA/Mick Speer]
NASA, in partnership with DOE, is developing and testing new fuels that use low-enriched uranium for space applications to see how they perform under the extreme thermal and radiation environments needed for nuclear thermal propulsion. NASA is working closely with DOE, industry, and universities to put fuel samples in research reactors at Idaho National Laboratory's Transient Reactor Test (TREAT) facility and the Massachusetts Institute of Technology Nuclear Reactor Laboratory for nuclear testing. The team is also performing non-nuclear testing in simulated reactors at Marshall test facilities.
"The reactor underpinning a nuclear thermal propulsion system is a significant technical challenge due to the very high operating temperatures needed to meet the propulsion performance goals," explained Anthony Calomino, NASA's nuclear technology portfolio lead within STMD.
While most of the engine operates at modest temperatures, materials in direct contact with the reactor fuel must be able to survive temperatures above 4,600 F. NASA and DOE have been working with industry on a viable approach, and industry is now developing preliminary designs to meet this challenge.
Read more NASA articles about Moon to Mars missions at nasa.gov/topics/moon-to-marsreports.
Sources: Compiled from NASA reports by Sarah Frazier and Clare Skelly, NASA Headquarters, Washington, and Tabatha Thompson, DARPA.
Published March 2023
Rate this article
View our terms of use and privacy policy

